IP Allocation failure during onboarding
Issue/Introduction
Symptoms:
- When Onboarding a virtual machine, the IP Address allocation phase is skipped
- When attempting to deploy a new VM from vRA, an IP conflict occurs with a previous onboarded VM
Environment
VMware vRealize Automation 8.x
Cause
IP conflict occurs because the onboarded VM's IP address was not allocated within vRA.
Resolution
VMware is aware of this issue.
In order to avoid IP conflicts in vRA, follow the steps below before onboarding VMs.
Important: The Prerequisites before onboarding are required even when there are no IP conflicts in the environment.
Workaround:
Note: To query for allocated IP Addresses, run the following API query
https://vRAFQDN/provisioning/uerp/resources/ip-addresses?expand=true&$filter=(ipAddress eq 'IPADDRESS') and (ipAddressStatus eq 'ALLOCATED')Where IPADDRESS is italicized and is required to be updated with the IP Address you wish to check for.
New provisioned VMs with IP Conflicts
In case you have new provisioned VMs with IP conflict before applying the workaround follow the next steps.- Delete the newly provisioned VM
- Release the IP
- Ensure IP Address is in ‘Available’ status (To verify in: Infrastructure > Resources > Networks > IP Addresses)
- Unregister the previously onboarded VM
- Delete the deployment whose resources were unregistered. To perform this operation only after ensuring VMs were successfully unregistered and back in ‘Discovered’ state. Discovered state can be verified under Virtual Machines tab.
If you do not have any IP conflicts proceed with the following steps.
Prerequisites before onboarding
- Ensure an address of the discovered VM is data collected: Cloud Assembly > Resources > Virtual Machines > Address
- Create a valid subnetRange if you have not already done so: Infrastructure > Resources > Networks > IP Ranges Note: when a vSphere cloud account is associated with an NSX instance then subnets need to be created in vRA for NSX networks for allocation to succeed during onboarding.
- In case of external IPAM onboarding, in addition to the above, add the below custom properties to the VM before executing the onboarding plan
__Infoblox.IPAM.Migration.ExtensibilityKey __IPAM.Migration.ExtensibilityKey whose values are the resourceIds of the VM
Note: A ResouceId can be found and retrieved from Infoblox under the extensible attributes similar to the screenshot provided.
Note: This step will ensure the deallocate IP to Infoblox occurs when the VM is deleted in vRA.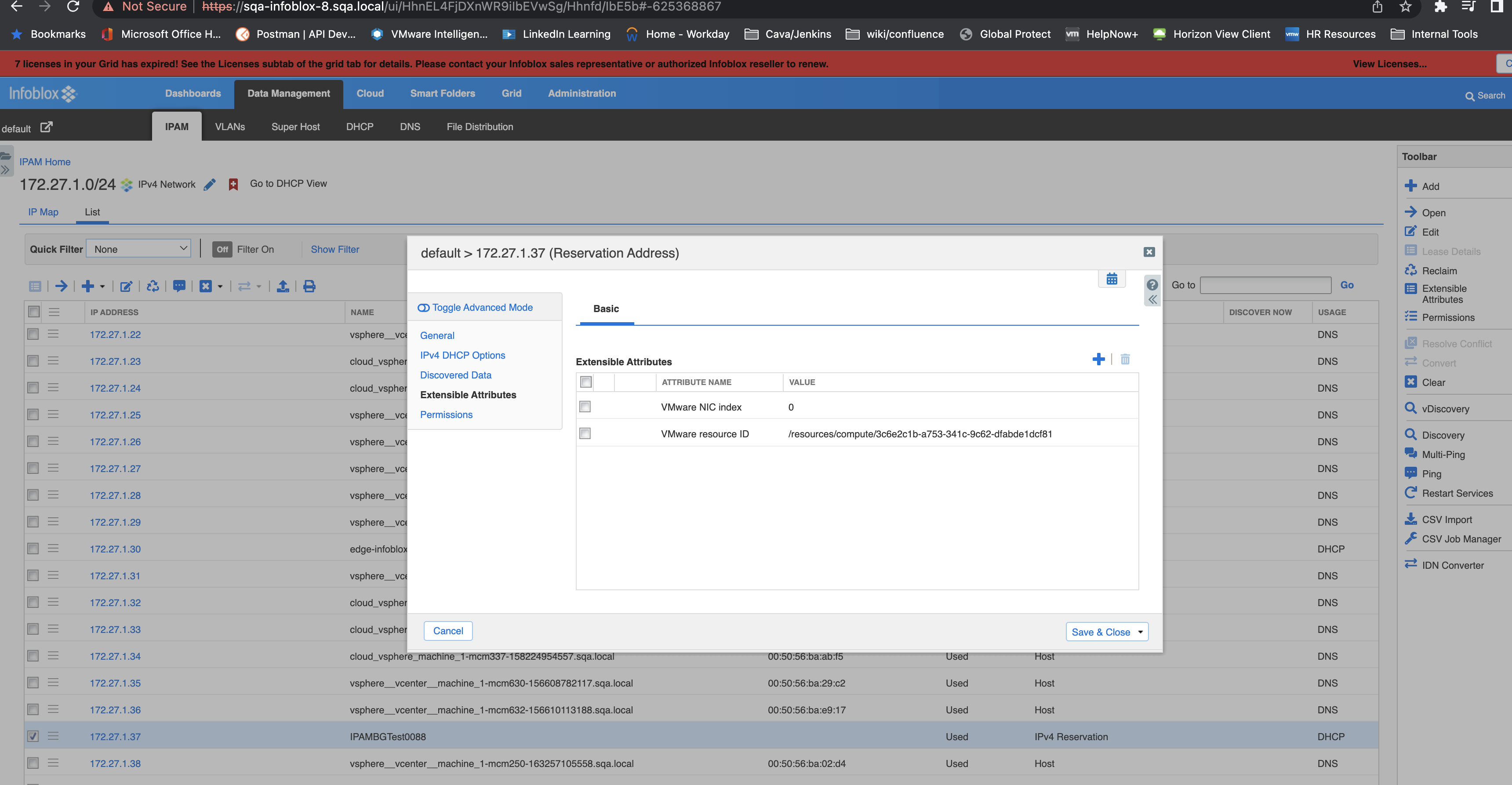
Note: This step will ensure the deallocate IP to Infoblox occurs when the VM is deleted in vRA.
- Add the discovered VM to the onboarding plan and run it. Network should be onboarded and IP should become allocated.
- Verify the IP is now allocated: Infrastructure > Resources > Networks > IP Addresses
Additional Information
Impact/Risks:
This can lead to IP conflicts on your network when provisioning new virtual machines.
This can lead to IP conflicts on your network when provisioning new virtual machines.
Comments
Post a Comment